Continental Drift the Geological Jigsaw
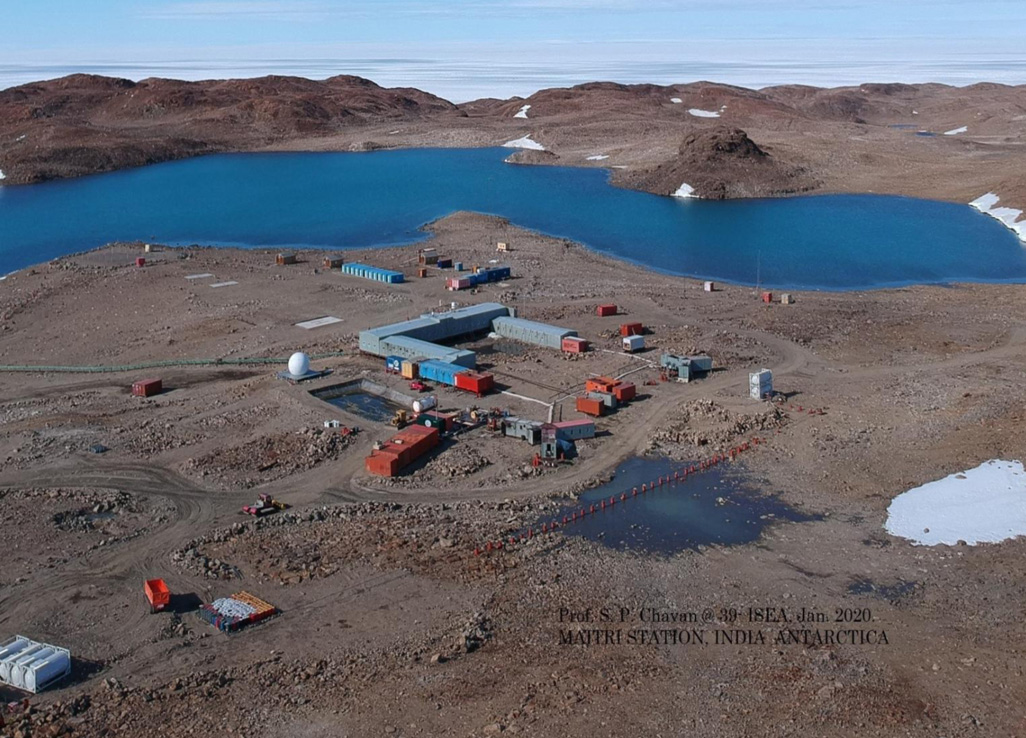



India is set to embark on a new chapter in its Polar exploration journey with the construction of Maitri II. The Indian government plans to establish a new research station near the existing Maitri ba...
.png )
The Deep Ocean Mission (DOM), approved by the Government of India in 2021 under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), represents a strategic step in realizing Sustainable Development Goal 14 (SDG 14:...

China recently announced restrictions on the export of seven rare earth elements (REEs), soon after US President Donald Trump decided to impose tariffs. As the world's dominant supplier—responsible fo...
The jigsaw fit, one of the strongest evidences of Continental Drift Theory was propagated by A Wegener in 1912. Although remarked upon way back in 1620, with several scientists believing that the pres...
The Indian plate, separated from the Antarctic, started moving to the north northeast about 180 million years ago. The present day movement of the Indian plate from the Carlsberg spreading ridge resul...
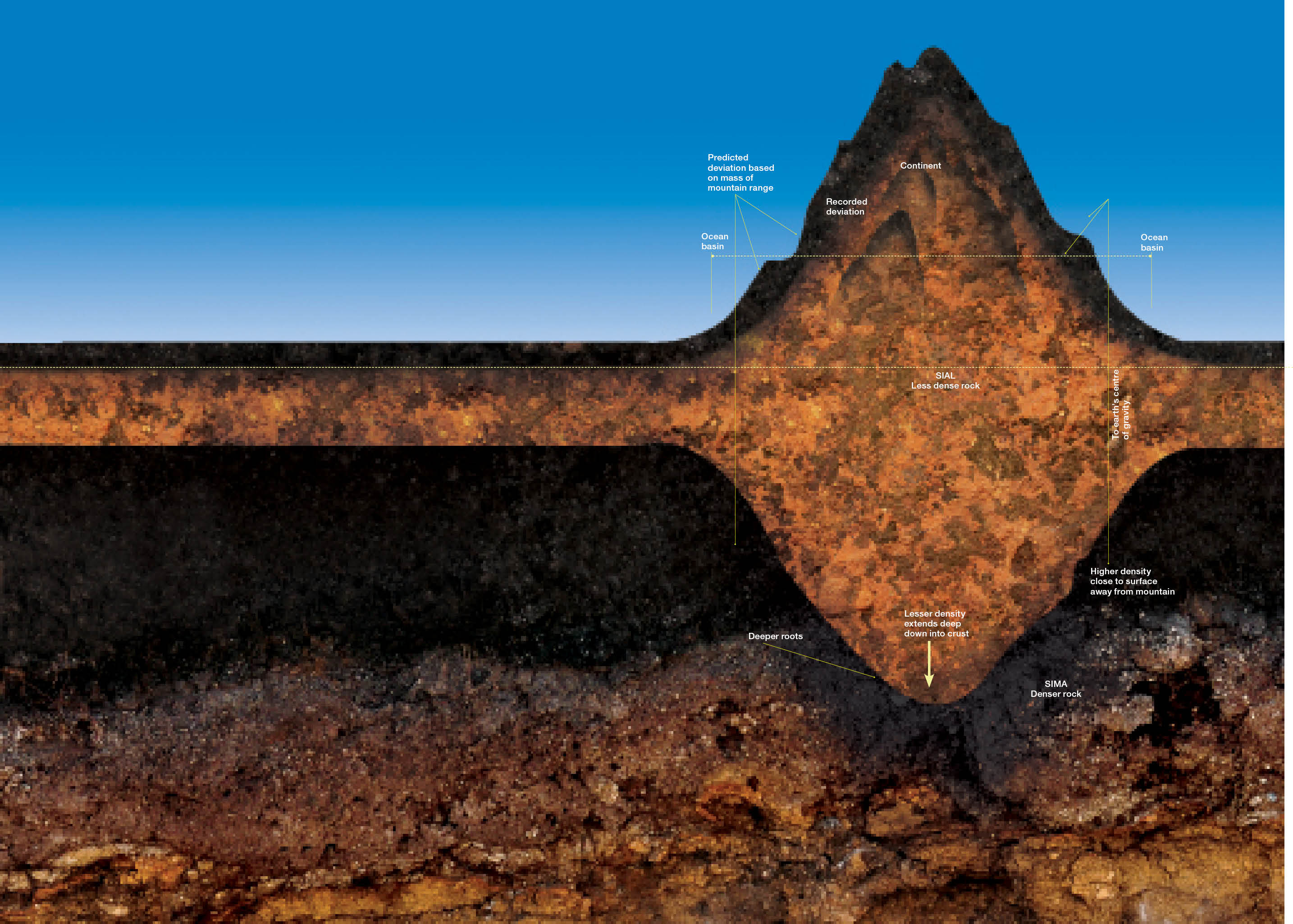
Earth’s crust is relatively lighter as compared to the denser mantle over which it lies and therefore behaves as if it is floating. Areas of the earth’s crust rise or subside to accommodate added load...
In recent years it has been possible to explore geological activity on the deep ocean floor. Using a submersible research vessel such as the United States’ Alvin, scientists have been able to make per...
The jigsaw fit, one of the strongest evidences of Continental Drift Theory was propagated by A Wegener in 1912. Although remarked upon way back in 1620, with several scientists believing that the present day continents were the fragmented pieces of preexisting larger landmasses (supercontinents), it was only in the 1920s that the Theory gained prominence.

The Indian plate, separated from the Antarctic, started moving to the north northeast about 180 million years ago. The present day movement of the Indian plate from the Carlsberg spreading ridge results in collision in the Himalaya and subduction in the Andaman-Sumatra. These plate margins, therefore, are the major seismic belts of the moving Indian plate.
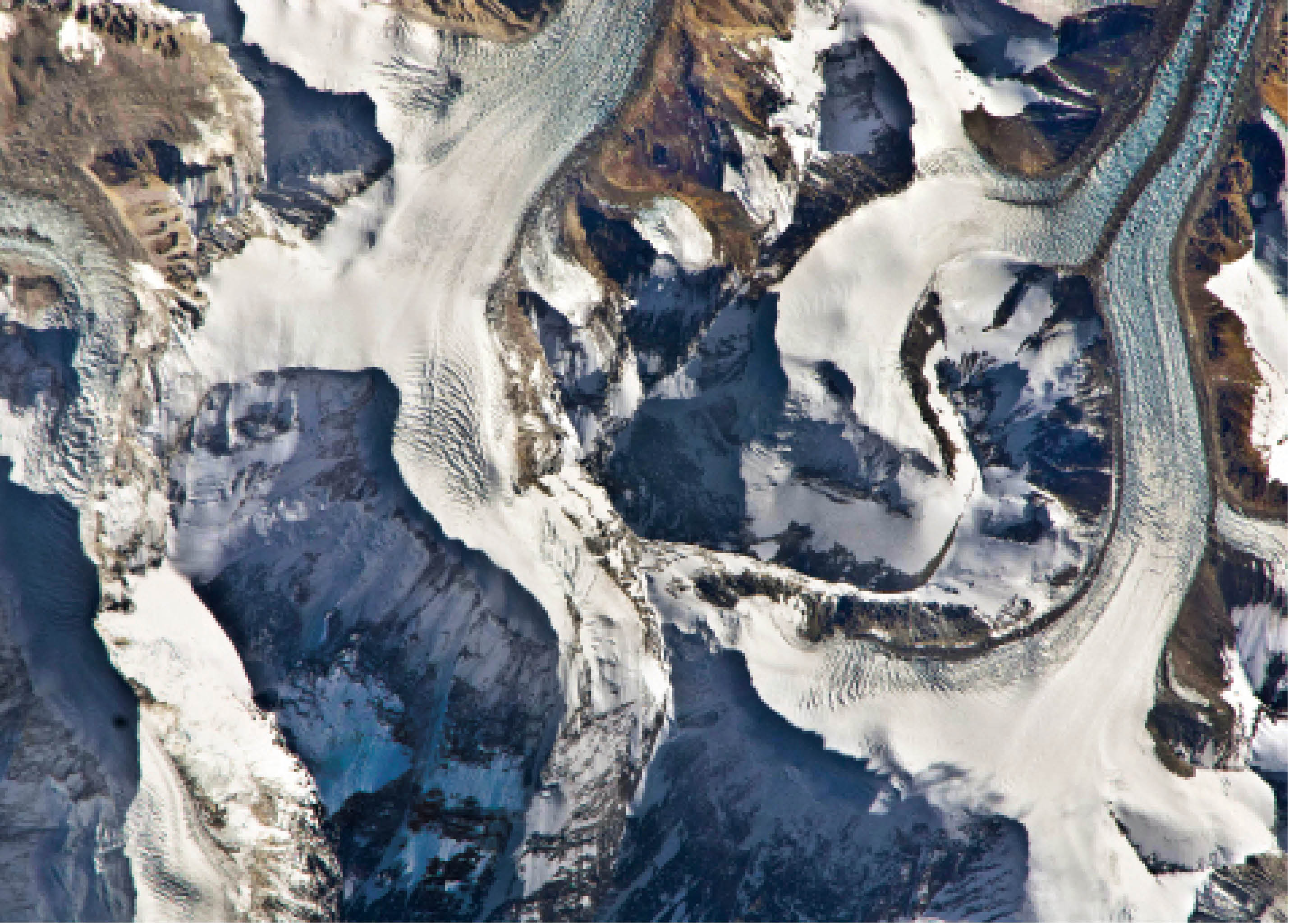

Earth’s crust is relatively lighter as compared to the denser mantle over which it lies and therefore behaves as if it is floating. Areas of the earth’s crust rise or subside to accommodate added load so that the forces that elevate landmasses balance the forces that depress them.